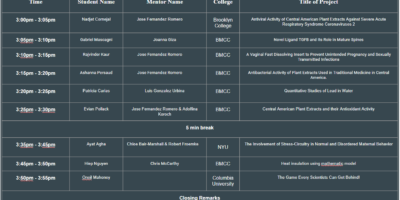
Author:
Mentor:
Jose A. Fernandez Romero PhD
Abstract:
Bacteria develop antibiotic resistance because of their ability to evolve and the misuse of marketable antimicrobial medicines. Because of this, there is an urgent need to discover new antimicrobial agents to help fight this resistance issue. The use of medicinal plants is part of human history and still is considered a vital source to identify new antimicrobial agents. We investigated four ethanolic plant extracts (Theobroma cacao, Bourreria huanita, Elettaria cardamomum, and Eriobotrya japonica), from plants widely used in Central America, for their ability to inhibit gram-negative (Escherichia coli) and gram-positive (Staphylococcus epidermidis) bacteria. The antibacterial activity was evaluated using the disk diffusion assay and the activity in a broth that measures bacterial growth over time using spectrophotometry. The disk diffusion assay showed no inhibition for any plant extracts tested, whereas the chloramphenicol control showed the expected inhibition indicating that S. epidermidis (23 mm halo) and E. coli (22 mm halo) were susceptible. On the other hand, the antibacterial method that monitors bacterial growth over time showed significant inhibition of E. coli and S. epidermidis growth by E. japonica ethanolic extract (p<0.001). Additionally, ethanolic extract of T. cacao and E. cardamomum showed significant inhibition of S. epidermidis growth (p<0.001). Our results warrant further investigation of the antibacterial properties of these plant extracts.